ログアウトされました
脳神経外科
水頭症と脳圧管理
重力可変式バルブは治療効果を高めます

医療従事者の確認
この先は、医療従事者の方を対象とした情報を提供しております。 大変申し訳ございませんが、医療従事者の方以外はご遠慮ください。
あなたは医療従事者ですか?
確認 はい、わたしは医療従事者です. キャンセル いいえ、わたしは医療従事者ではありません.
水頭症治療用シャント、神経内視鏡
水頭症の治療では、過剰な脳脊髄液(CSF)を体の他の部位に排出するために、シャントシステムが留置されることが一般的です。脳脊髄液の過剰な蓄積によって上昇した頭蓋内圧を正常範囲に戻し、脳の損傷を防ぎます。
シャント手術に代わる方法として、内視鏡的第三脳室開窓術(ETV)があります。シャントシステムを留置する代わりに、外科的に第三脳室の底に穴を開け、脳脊髄液(CSF)を流し、吸収されるようにする方法です。エースクラップは様々な神経内視鏡システムを提供しています: MINOP®、MINOP® InVent
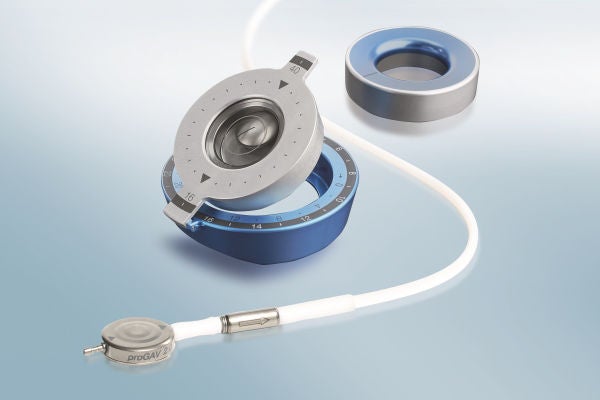
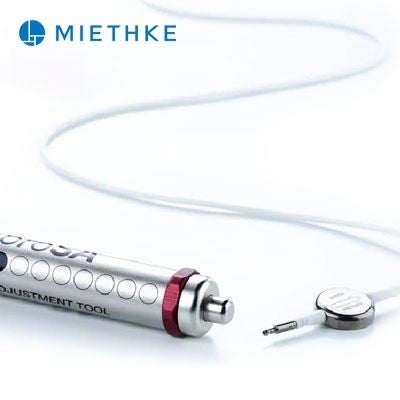
ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブは、姿勢の変化によって生じるオーバードレナージやアンダードレナージといった合併症を防ぐための機構を備えています。これにより良好な治療効果を発揮し、オーバードレナージの発生を減少させます。[1-4]すべてのミートケ社製シャントバルブは、チタン製で精密に製造されています。また、3テスラ以下の磁場において、開放圧が意図せず変更されないように設計されています。[5]
水頭症と脳圧管理
製品ポートフォリオ
水頭症と脳圧管理
関連製品
Digital applications
MIETHKE HC&ME App – Patient diary app
Google Play preview and free download >>
Google Play preview and free download >>
[1] Tschan CA, Antes S, Huthmann A, et al. Overcoming CSF overdrainage with the adjustable gravitational valve proSA. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2014;156(4):767-76; discussion 776.
[2] Suchorska B, Kunz M, Schniepp R, et al. Optimized surgical treatment for normal pressure hydrocephalus: comparison between gravitational and differential pressure valves. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2015;157(4):703-9.
[3] Lemcke J, Meier U, Muller C, et al. Safety and efficacy of gravitational shunt valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a pragmatic, randomised, open label, multicentre trial (SVASONA). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84(8):850-7
[4] Sprung C, Schlosser HG, Lemcke J, et al. The adjustable proGAV shunt: a prospective safety and reliability multicenter study. Neurosurgery. 2010;66(3):465-74.
[5] Chari A, Czosnyka M, Richards HK, Pickard JD, Czosnyka ZH. Hydrocephalus shunt technology: 20 years of experience from the Cambridge Shunt Evaluation Laboratory. J Neurosurg. 2014;120(3):697-707.
[6] Antes S, Stadie A, Muller S, et al. Intracranial Pressure-Guided Shunt Valve Adjustments with the Miethke Sensor Reservoir. World Neurosurg. 2018;109:e642-e50.
[7] Freimann FB, Schulz M, Haberl H, et al. Feasibility of telemetric ICP-guided valve adjustments for complex shunt therapy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30(4):689-97.
[8] Thompson S, Thorne L, Toma A, et al. Telemetric monitoring of ICP within a shunt system. A single centre experience including the first in vivo comparison versus conventional intraparenchymal monitoring. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. 2017;14(Suppl 1):A63.
My B. Braun とのつながりを保つ
パーソナライズされたアカウントで、オンライン体験がより簡単、快適、安全になります。